Quantum Leap: The Transformative Future of Quantum Computing
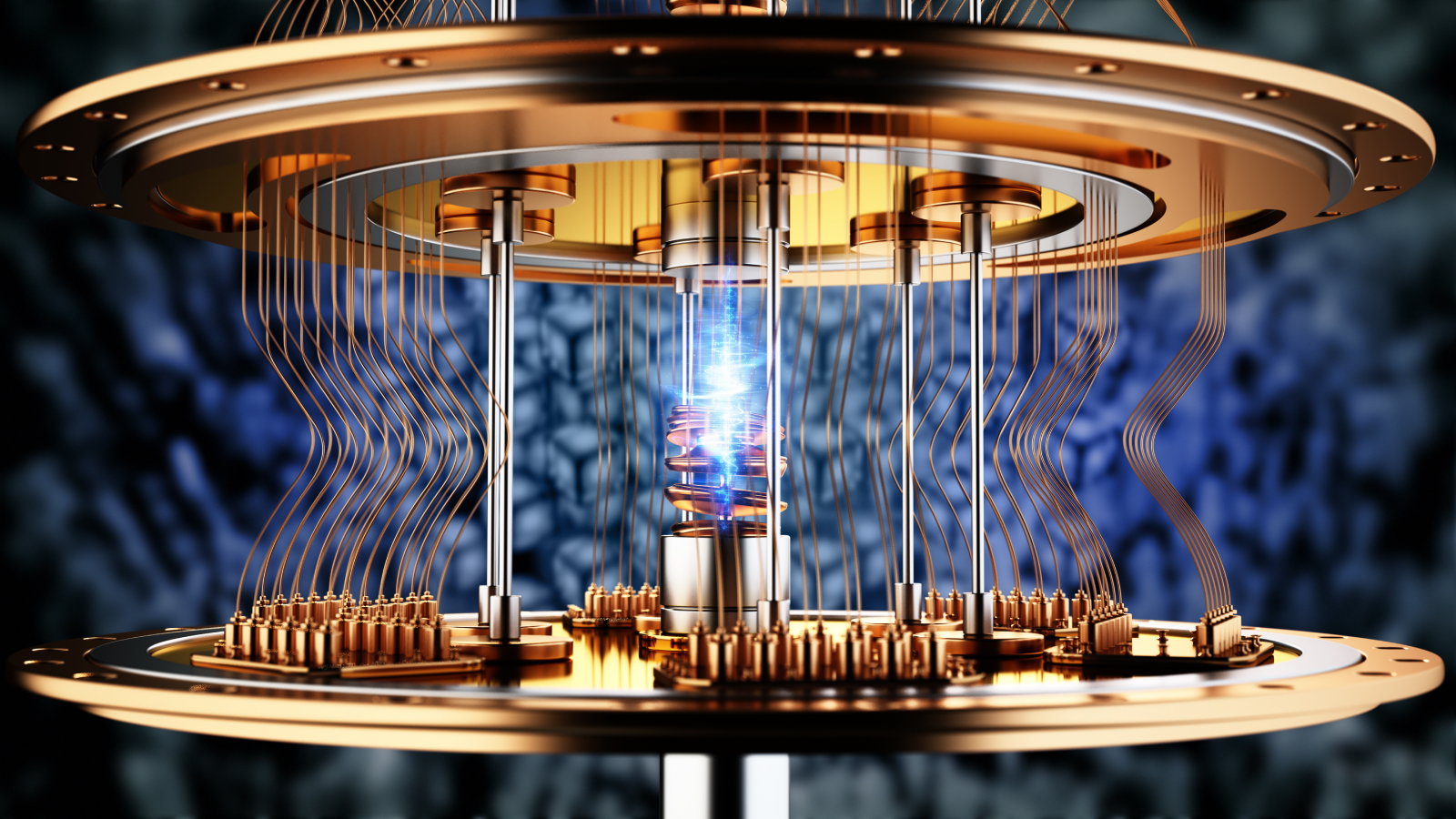
As quantum computing edges closer to commercial viability, experts predict a revolution across industries, from cryptography to pharmaceuticals.
The Quantum Leap: Exploring the Future of Quantum Computing in 2026
As we step into 2026, quantum computing stands on the brink of revolutionizing industries with its unparalleled processing power. Experts weigh in on the potential and challenges of this groundbreaking technology.